BOURSESSENEGAL – Enterococcus faecalis is a bacteria that plays a significant role in human health and disease. While often overlooked, this organism is both a beneficial member of our gut microbiome and a potential pathogen that can cause infections. In this blog post, we will explore what its functions, its implications in health and disease, and how to manage its presence in our bodies.
What is Enterococcus Faecalis?
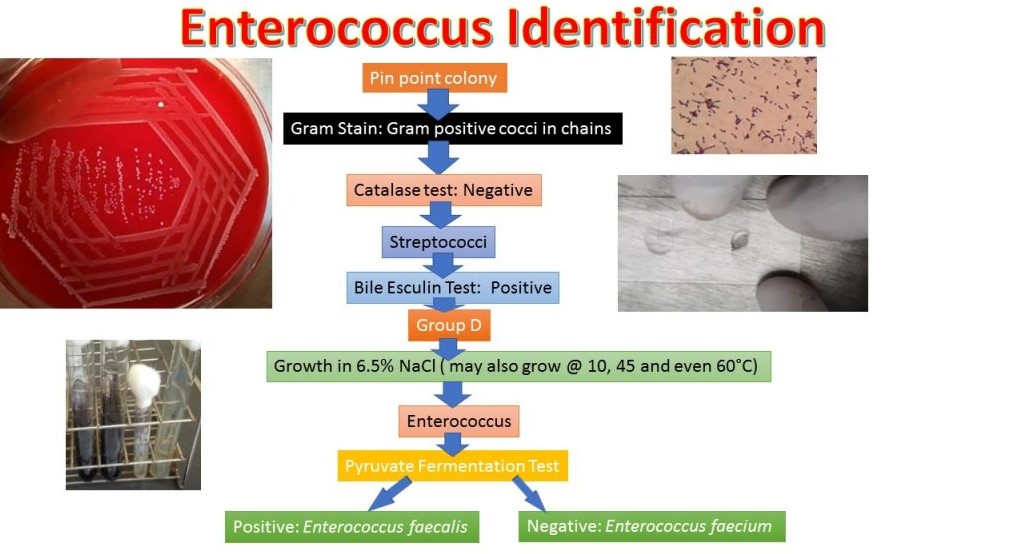
Enterococcus faecalis is a Gram-positive bacterium that belongs to the Enterococcus genus. This organism typically resides in the intestines of humans and animals. As part of the gut flora, contributes to various functions, including digestion and nutrient absorption. However, it can also act as an opportunistic pathogen, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Characteristics of Enterococcus Faecalis
Enterococcus faecalis is known for its resilience. It can survive harsh environments, including high salt concentrations and extreme temperatures. This adaptability allows it to thrive in diverse settings, making it an interesting subject of study in microbiology and medicine.
The Role of Enterococcus Faecalis in the Human Body
1. Beneficial Functions
In a healthy gut, Enterococcus faecalis helps maintain a balanced microbiome. It aids in digestion, particularly in breaking down complex carbohydrates. Additionally, it can produce substances like bacteriocins, which inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria. This protective role is essential for overall gut health.
2. Potential Pathogenicity
Despite its beneficial aspects, Enterococcus faecalis can become problematic. In certain conditions, it can cause infections, particularly in hospitals. Common infections associated with this bacterium include urinary tract infections, endocarditis, and wound infections. Understanding the circumstances that allow this transition is crucial for prevention and treatment.
Infections Caused by Enterococcus Faecalis
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Enterococcus faecalis is a significant cause of UTIs, especially in patients with catheter use or urinary tract abnormalities. Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain and may require antibiotic treatment.
2. Endocarditis
This bacterium can infect the heart valves, leading to endocarditis, a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. Individuals with pre-existing heart conditions or weakened immune systems are at higher risk.
3. Wound Infections
Enterococcus faecalis can also be implicated in wound infections, particularly in surgical sites. Proper wound care and hygiene practices are essential in preventing these infections.
Risk Factors for Enterococcus Faecalis Infections
1. Weakened Immune System
Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or with HIV, are more susceptible to infections caused by.
2. Hospitalization
Healthcare settings often see a higher prevalence of this bacterium. Patients with prolonged hospital stays or those who have undergone invasive procedures are at increased risk.
3. Antibiotic Use
Overuse or misuse of antibiotics can disrupt the normal gut flora, allowing to thrive and potentially lead to infections.
Diagnosis of Enterococcus Faecalis Infections
1. Laboratory Testing
Diagnosing an infection caused by typically involves laboratory tests. Healthcare providers may collect samples from urine, blood, or wounds and culture them to identify the presence of the bacteria.
2. Sensitivity Testing
Once identified, the lab performs sensitivity testing to determine which antibiotics will effectively treat the infection. This step is crucial, as can be resistant to many commonly used antibiotics.
Treatment Options for Enterococcus Faecalis Infections
1. Antibiotics
The primary treatment for infections caused by is antibiotics. However, treatment can be challenging due to antibiotic resistance. Commonly used antibiotics include ampicillin and vancomycin, but the choice of medication depends on sensitivity results.
2. Supportive Care
In addition to antibiotics, supportive care is essential. This may involve hydration, pain management, and addressing any underlying conditions contributing to the infection.
3. Monitoring and Follow-Up
Patients receiving treatment for infections require close monitoring. Regular follow-up appointments help ensure the infection resolves and that no complications arise.
Preventing Enterococcus Faecalis Infections
1. Good Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene is crucial in preventing infections. Regular handwashing, especially in healthcare settings, can reduce the spread of this bacterium.
2. Responsible Antibiotic Use
Using antibiotics only when necessary helps preserve the effectiveness of these medications. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s guidance regarding antibiotic prescriptions.
3. Safe Hospital Practices
Hospitals can reduce the risk of infections by implementing strict infection control measures. This includes proper sterilization of medical equipment and monitoring for signs of infection in patients.
The Future of Research on Enterococcus Faecalis
1. Understanding Resistance Mechanisms
As antibiotic resistance becomes a growing concern, research continues to focus on understanding the mechanisms that allow to resist treatment. This knowledge will be vital in developing new therapeutic strategies.
2. Exploring Probiotic Potential
Given its role in the gut, some researchers are exploring the potential of using as a probiotic. This research aims to leverage its beneficial aspects while minimizing pathogenic risks.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of Enterococcus Faecalis
is a fascinating bacterium with both beneficial and harmful roles in human health. While it contributes positively to our gut microbiome, it can also cause serious infections, particularly in vulnerable populations.
By understanding how to manage its presence, from practicing good hygiene to responsible antibiotic use, we can harness the positive aspects of while minimizing its risks. Stay informed and proactive in your health journey, and don’t hesitate to consult healthcare professionals regarding any concerns related to this intriguing bacterium.
REFERENCE : ran303