Hernias can affect anyone, and understanding what they are is crucial for prevention and treatment. A hernia occurs when an organ or fatty tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. This condition can cause discomfort and lead to more serious complications if not addressed properly. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of hernias, their symptoms, and available treatment options.
What Causes a Hernia?
Hernias can result from various factors. They often develop due to a combination of muscle weakness and strain. Here are some common causes:
- Congenital Factors: Some people are born with weakened muscles that can lead to hernias later in life.
- Aging: As we age, our muscles weaken, making it easier for hernias to develop.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put additional strain on the abdominal wall.
- Heavy Lifting: Repeatedly lifting heavy objects without proper technique can cause hernias.
- Chronic Coughing or Sneezing: Conditions like asthma can lead to increased pressure on the abdominal wall.
Understanding these causes helps you recognize risk factors and take preventive measures.
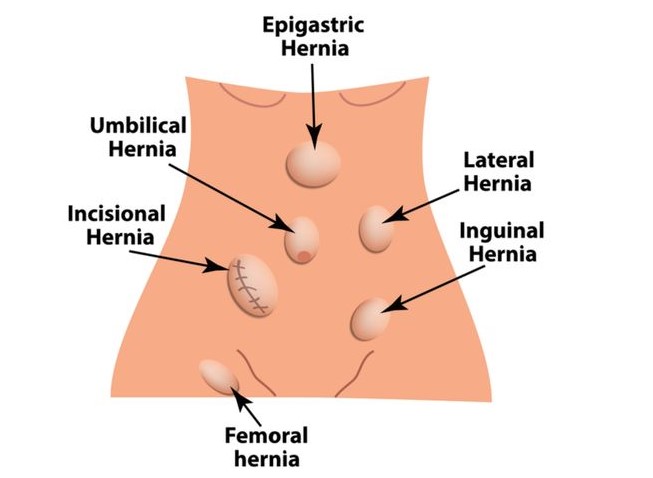
Types of Hernias
There are several types of hernias, each varying in location and symptoms:
Inguinal Hernia
The most common type, an inguinal hernia occurs when tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the groin. This type is more prevalent in men and can cause swelling or a bulge in the groin area.
Femoral Hernia
Femoral hernias appear just below the groin, where the femoral artery passes into the thigh. This type is less common but can be particularly dangerous for women.
Umbilical Hernia
Umbilical hernias occur when tissue bulges through the abdominal wall near the belly button. They are common in infants but can also affect adults, especially those who are overweight.
Hiatal Hernia
This type occurs when a portion of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. Hiatal hernias can lead to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), causing heartburn and discomfort.
Incisional Hernia
An incisional hernia can occur at the site of a previous surgical incision. This type can develop if the surgical site weakens over time.
Epigastric Hernia
An epigastric hernia occurs when fat tissue pushes through the abdominal wall between the belly button and the chest. This type may not always cause noticeable symptoms.
Symptoms of Hernias
Recognizing the symptoms of a hernia is essential for timely treatment. Common signs include:
- Bulging: A noticeable bulge or lump in the affected area, which may disappear when lying down.
- Discomfort or Pain: A feeling of pressure, discomfort, or pain, especially during physical activities, lifting, or coughing.
- Weakness or Heaviness: A sensation of weakness or heaviness in the abdomen or groin.
- Nausea or Vomiting: In severe cases, especially with incarcerated or strangulated hernias, nausea or vomiting may occur.
If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Hernias
Healthcare providers typically diagnose hernias through a physical examination. During the exam, they will check for bulges or abnormalities in the affected area. Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI, may be utilized to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the hernia.
Treatment Options for Hernias
The treatment approach for hernias depends on the type, severity, and symptoms. Here are the most common options:
Watchful Waiting
For some patients with small, asymptomatic hernias, doctors may recommend a watchful waiting approach. This means monitoring the hernia without immediate intervention.
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle adjustments can help manage symptoms and prevent hernias from worsening. These changes include:
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces strain on the abdominal wall.
- Avoiding Heavy Lifting: If you have a history of hernias, avoid lifting heavy objects or use proper lifting techniques.
- Dietary Adjustments: Eating smaller meals and avoiding spicy foods can help manage symptoms of hiatal hernias.
Surgical Repair
In many cases, surgery is the most effective treatment for hernias. Surgical options include:
- Open Surgery: This traditional approach involves making a larger incision to repair the hernia.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive technique where small incisions are made, and the hernia is repaired using a camera and specialized instruments.
- Hernia Mesh Repair: In both surgical methods, a mesh may be placed over the weak spot to reinforce the abdominal wall.
Recovery from Hernia Surgery
Recovery time varies depending on the surgical method used. Generally, patients can expect to return to normal activities within a few weeks. Follow your doctor’s post-operative care instructions to ensure a smooth recovery.
Complications Associated with Hernias
If left untreated, hernias can lead to serious complications. These include:
Incarcerated Hernia
An incarcerated hernia occurs when the tissue becomes trapped and cannot be pushed back into the abdomen. This can lead to severe pain and discomfort.
Strangulated Hernia
This serious condition occurs when the blood supply to the trapped tissue is cut off. A strangulated hernia can lead to tissue death and requires immediate medical attention.
Preventing Hernias
While not all hernias are preventable, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Strengthening Core Muscles: Engaging in exercises that strengthen the core can help support the abdominal wall.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Staying within a healthy weight range reduces strain on the abdominal area.
- Using Proper Lifting Techniques: Always lift with your legs, not your back, to minimize stress on the abdominal wall.
Conclusion
Understanding hernias is essential for prevention and effective treatment. Recognizing the symptoms and types can empower you to seek timely medical attention. If you suspect you have a hernia, consult a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and treatment options. By taking proactive steps, you can manage your health and reduce the risk of complications. Stay informed, and prioritize your well-being!
REFERENCE : gacorx5000