BOURSESSENEGAL – Monitoring your blood pressure is crucial for maintaining good health. A blood pressure chart serves as a valuable tool to help you understand your readings and manage your cardiovascular health effectively. In this guide, we will explore what a blood pressure chart is, how to read it, the different categories of blood pressure, and tips for maintaining healthy levels.
What is a Blood Pressure Chart?
A blood pressure chart is a visual representation of the various ranges of blood pressure readings. It helps you understand what your numbers mean and where you stand regarding your cardiovascular health. Blood pressure measurements consist of two numbers: systolic (the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats) and diastolic (the pressure when your heart rests between beats). The chart categorizes these measurements into different levels, helping you assess whether your blood pressure is normal, elevated, or indicative of hypertension.
The Importance of Monitoring Blood Pressure
Monitoring your blood pressure regularly is essential for several reasons. First, high blood pressure often has no symptoms, meaning many people are unaware they have it. Secondly, untreated high blood pressure can lead to serious health issues such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage. By using a blood pressure chart, you can track your numbers and take proactive steps to maintain a healthy level.
How to Read a Blood Pressure Chart
Understanding the Basics
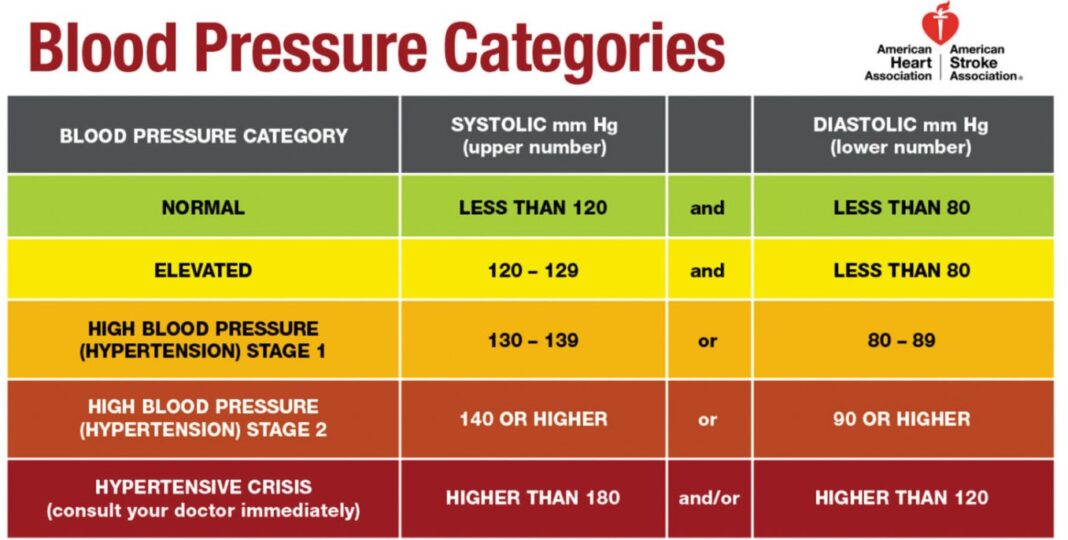
The blood pressure chart typically divides readings into different categories:
- Normal: Systolic less than 120 and diastolic less than 80
- Elevated: Systolic between 120-129 and diastolic less than 80
- Hypertension Stage 1: Systolic between 130-139 or diastolic between 80-89
- Hypertension Stage 2: Systolic 140 or higher or diastolic 90 or higher
- Hypertensive Crisis: Systolic higher than 180 and/or diastolic higher than 120 (requires immediate medical attention)
Interpreting Your Readings
To effectively use the blood pressure chart, start by measuring your blood pressure with a reliable device. Note both the systolic and diastolic numbers. Once you have your readings, refer to the chart to determine which category your numbers fall into. Understanding where you stand can empower you to make informed health decisions.
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure Readings
Several factors can influence your blood pressure readings. Here’s a closer look:
1. Age and Gender
As people age, their blood vessels become stiffer, leading to higher blood pressure. Men are more likely to develop high blood pressure earlier in life compared to women. However, after menopause, women’s risk increases.
2. Lifestyle Choices
Diet plays a crucial role in blood pressure management. A diet high in salt, sugar, and saturated fats can raise blood pressure levels. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports heart health.
3. Physical Activity
Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and can lower blood pressure. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week to keep your heart in top shape.
4. Stress Levels
Chronic stress can contribute to high blood pressure. Finding effective stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can help keep your levels in check.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Blood Pressure
1. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
Focus on consuming foods rich in potassium, magnesium, and fiber. These nutrients can help lower blood pressure. Incorporate plenty of:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for at least five servings a day.
- Whole Grains: Choose brown rice, oats, and whole grain bread.
- Lean Proteins: Opt for fish, poultry, beans, and legumes.
2. Limit Sodium Intake
Reducing sodium in your diet is crucial for blood pressure management. The American Heart Association recommends limiting sodium to less than 2,300 mg per day, and ideally, aiming for 1,500 mg.
3. Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water is vital for maintaining healthy blood pressure. Dehydration can cause blood vessels to constrict, leading to higher readings.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight increases your risk of developing high blood pressure. If you’re overweight, losing even a small amount of weight can help reduce your blood pressure significantly.
5. Exercise Regularly
Engaging in regular physical activity strengthens your heart and improves blood circulation. Even simple activities like walking or cycling can make a difference.
6. Manage Stress
Finding effective ways to manage stress can significantly impact your blood pressure. Techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing, and physical activity can reduce stress levels.
When to Consult a Doctor
If you notice consistently high readings on your blood pressure chart, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. Additionally, seek medical advice if you experience symptoms such as:
- Severe headaches
- Blurred vision
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
These symptoms may indicate a hypertensive crisis or other serious health conditions requiring immediate attention.
Blood Pressure Monitoring at Home
Choosing the Right Device
Investing in a reliable blood pressure monitor is crucial for tracking your readings at home. Look for devices that are:
- Validated: Ensure they meet clinical standards.
- Easy to Use: Choose a device with a clear display and straightforward instructions.
- Cuff Size: Select a cuff that fits your arm correctly for accurate readings.
How to Measure Blood Pressure at Home
- Prepare: Sit quietly for at least five minutes before taking your reading. Ensure you’re in a comfortable position.
- Position the Cuff: Wrap the cuff around your upper arm, making sure it’s snug but not too tight.
- Take the Reading: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to get an accurate measurement.
- Record Your Numbers: Keep a log of your readings, noting the date and time. This information can help your doctor make informed decisions about your health.
Conclusion
Understanding your blood pressure is vital for maintaining your health and preventing serious complications. A blood pressure chart is an essential tool in this journey. By monitoring your readings, making informed lifestyle choices, and consulting healthcare professionals when needed, you can take control of your cardiovascular health.
Don’t underestimate the importance of regular check-ups and monitoring. Empower yourself with knowledge about your blood pressure, and take proactive steps to ensure a healthier future. Whether you’re managing existing conditions or aiming to prevent them, staying informed is key. So, grab that blood pressure chart and start your journey toward better health today!
REFERENCE : nirwana4d