BOURSESSENEGAL – When it comes to sexual health, few topics evoke as much concern as flesh-eating STD. These infections, while rare, can have severe consequences if left untreated. Understanding their causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies is crucial for maintaining your health and well-being. In this post, we will explore what flesh-eating STDs are, how they spread, their effects on the body, and the steps you can take to protect yourself.
What Are Flesh-Eating STD?
Definition and Overview
Flesh-eating STD refer to a group of sexually transmitted infections that can lead to necrotizing fasciitis—a severe bacterial infection that destroys skin, fat, and tissue. The most notable bacteria associated with this condition are Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus. These infections can rapidly progress and may require immediate medical intervention.
Common Types of Flesh-Eating STD
While there are several STDs, not all cause flesh-eating conditions. However, certain infections can lead to necrotizing fasciitis if bacteria enter the bloodstream or tissues. Some notable ones include:
- Syphilis: In advanced stages, syphilis can lead to serious complications, including skin lesions that may become infected.
- Gonorrhea: Untreated gonorrhea can lead to systemic infections, potentially resulting in tissue destruction.
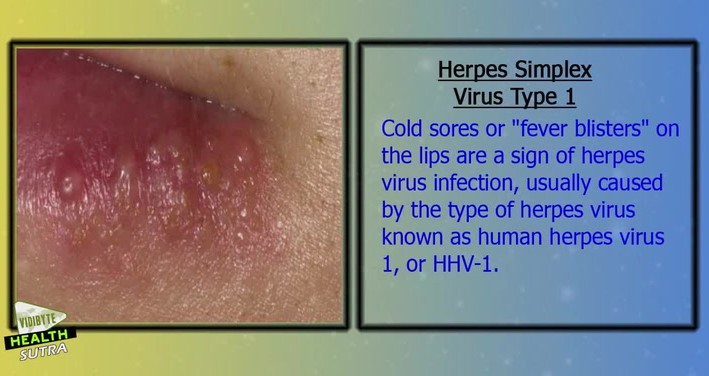
- Herpes Simplex Virus: Severe cases of herpes can lead to infections that may affect surrounding tissues, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
Symptoms of Flesh-Eating STD
Early Warning Signs
Recognizing the symptoms of flesh-eating STDs can be life-saving. Early indicators include:
- Unusual Skin Changes: Redness, swelling, or pain in the affected area.
- Fever: A sudden onset of high fever often accompanies an infection.
- Rapid Tissue Deterioration: Visible signs of tissue decay can appear within hours.
Advanced Symptoms
If left untreated, symptoms can escalate quickly. Look out for:
- Severe Pain: Intense pain that seems disproportionate to the visible symptoms.
- Blisters or Ulcers: The appearance of blisters or open sores that worsen over time.
- Discoloration: Skin turning dark or black as it dies off.
How Do Flesh-Eating STD Spread?
Understanding Transmission
Flesh-eating STDs spread primarily through sexual contact with an infected person. This can occur through:
- Unprotected Sex: Engaging in sexual activities without protection increases the risk of contracting STDs.
- Skin-to-Skin Contact: Direct contact with open sores or lesions can transmit the bacteria.
- Open Wounds: If one partner has a cut or wound, and the other has an infection, transmission can occur.
Other Contributing Factors
Certain behaviors and conditions can heighten the risk of developing flesh-eating STDs:
- Immunocompromised State: Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to infections.
- Poor Hygiene: Lack of proper hygiene can facilitate bacterial growth and infection.
- Substance Abuse: Drug and alcohol abuse can impair judgment, leading to risky sexual behaviors.
Prevention Strategies for Flesh-Eating STD
Practicing Safe Sex
The most effective way to prevent the transmission of STDs is through safe sex practices:
- Use Condoms: Latex or polyurethane condoms can significantly reduce the risk of STD transmission.
- Limit Partners: Reducing the number of sexual partners lowers exposure risk.
- Get Tested Regularly: Routine testing helps detect infections early, allowing for timely treatment.
Maintaining Good Hygiene
Hygiene plays a vital role in preventing infections:
- Wash Thoroughly: Clean your genitals and surrounding areas before and after sexual activity.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, razors, or other personal items that may harbor bacteria.
Vaccination
Vaccines can help protect against certain STDs:
- HPV Vaccine: Protects against human papillomavirus, which can lead to other health complications.
- Hepatitis Vaccines: Vaccines for Hepatitis A and B can prevent these infections.
Treatment Options for Flesh-Eating STD
Seeking Medical Attention
If you suspect you have a flesh-eating STD, immediate medical care is essential. Early intervention can save lives. Your healthcare provider will likely:
- Perform Tests: Laboratory tests will confirm the diagnosis and identify the specific bacteria involved.
- Administer Antibiotics: High-dose intravenous antibiotics are typically required to treat the infection.
Surgical Intervention
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary:
- Debridement: Removing dead or infected tissue to halt the spread of the infection.
- Skin Grafting: Reconstructing damaged skin with grafts may be required as part of the recovery process.
Living with and Recovering from Flesh-Eating STD
Physical and Emotional Impact
Recovering from a flesh-eating STD can be challenging both physically and emotionally. Support from healthcare providers, family, and friends can make a significant difference. Here are a few tips for managing your recovery:
- Follow Medical Advice: Adhere strictly to your treatment plan and follow-up appointments.
- Stay Informed: Understanding your condition helps you manage your health better.
- Seek Counseling: Consider talking to a mental health professional to address any emotional struggles.
Long-Term Health Considerations
Even after treatment, you should continue to monitor your health. Regular check-ups will help ensure that there are no lingering effects or complications. Moreover, maintaining healthy lifestyle choices will support your overall recovery and well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding flesh-eating STD is crucial for safeguarding your sexual health. While they are rare, the consequences can be severe if left untreated. By practicing safe sex, maintaining good hygiene, and staying informed about your health, you can significantly reduce your risk. If you experience any concerning symptoms, seek medical attention immediately. Your health is paramount, and being proactive is your best defense against these infections.
flesh eating std
REFERENCE : shoot588