BOURSESSENEGAL – Muscle relaxers are medications that help relieve muscle spasms, tension, and discomfort. Whether you’ve experienced a sports injury, chronic pain, or a stressful day, muscle can offer significant relief. However, it’s essential to understand how these medications work, their types, and any potential side effects. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore muscle in detail, helping you make informed decisions about their use.
What Are Muscle Relaxers?
Muscle relaxers, also known as muscle relaxants, are a class of drugs that reduce muscle tone and spasms. They work by affecting the central nervous system (CNS) or directly influencing the muscles. Physicians often prescribe them for conditions like back pain, fibromyalgia, and acute muscle injuries. While they can provide relief, using muscle responsibly is crucial.
How Do Muscle Relaxers Work?
Muscle relaxers primarily fall into two categories: centrally acting muscle relaxants and peripherally acting muscle relaxants.
Centrally Acting Muscle Relaxants
These medications work by depressing the CNS. By doing so, they help to reduce muscle spasticity and pain. Common examples include:
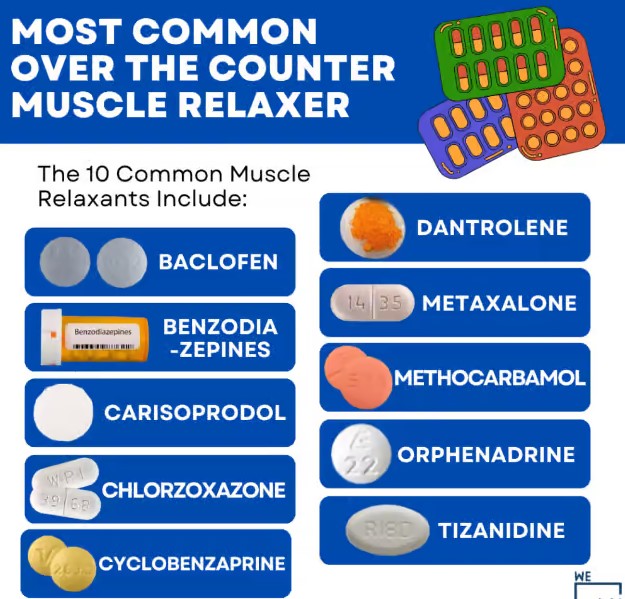
- Carisoprodol (Soma)
- Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril)
- Methocarbamol (Robaxin)
These medications are effective for short-term use, typically prescribed for acute muscle spasms or injuries.
Peripherally Acting Muscle Relaxants
Unlike their centrally acting counterparts, peripherally acting muscle relaxants target specific muscle groups. They block nerve impulses that lead to muscle contraction. One example is dantrolene (Dantrium), primarily used for severe muscle spasticity.
Common Uses of Muscle Relaxers
Muscle relaxers serve various purposes, making them valuable in different medical situations. Here are some common uses:
1. Relief from Acute Muscle Spasms
Injuries from sports or physical activity often lead to acute muscle spasms. Muscle relaxers help alleviate the pain and discomfort associated with these spasms, allowing for better movement and recovery.
2. Chronic Pain Management
For conditions like fibromyalgia or chronic lower back pain, muscle relaxers can provide much-needed relief. They reduce muscle tension, allowing patients to engage in daily activities with less discomfort.
3. Post-Surgical Recovery
After surgery, patients may experience muscle tension or spasms as part of the healing process. Muscle relaxers can help ease this discomfort, promoting relaxation and recovery.
4. Neurological Conditions
Certain neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, can lead to muscle stiffness and spasms. Muscle relaxers may be part of the treatment plan to improve mobility and comfort.
Types of Muscle Relaxers
Understanding the different types of muscle relaxers can help you choose the right medication for your needs. Here’s a breakdown of the most common options:
1. Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril)
Cyclobenzaprine is one of the most frequently prescribed muscle relaxers. It works by blocking nerve impulses in the brain, leading to reduced muscle spasms. Doctors often prescribe it for short-term relief from muscle pain.
2. Carisoprodol (Soma)
Carisoprodol is effective for treating acute muscle pain. It acts as a sedative, providing a calming effect that can help relieve discomfort. However, due to its potential for dependence, it’s usually prescribed for short periods.
3. Methocarbamol (Robaxin)
Methocarbamol is another popular choice for muscle spasms. It’s often used in combination with physical therapy. This medication works by depressing the CNS, helping to relax muscles.
4. Dantrolene (Dantrium)
Dantrolene is unique among muscle relaxers because it acts directly on muscle cells. It’s primarily used to treat severe muscle spasticity, particularly in conditions like multiple sclerosis or cerebral palsy.
5. Baclofen (Lioresal)
Baclofen is effective for managing spasticity caused by conditions like multiple sclerosis. It works by affecting the CNS, leading to muscle relaxation. Doctors may prescribe it in oral form or via an intrathecal pump for more severe cases.
Potential Side Effects of Muscle Relaxers
While muscle relaxers can provide significant relief, they come with potential side effects. Understanding these risks is vital for safe use.
Common Side Effects
- Drowsiness: Many muscle relaxers can cause sedation, making it unsafe to drive or operate heavy machinery.
- Dizziness: Users may experience dizziness or lightheadedness, especially when standing up quickly.
- Dry Mouth: This is a common side effect that can lead to discomfort.
Serious Side Effects
In rare cases, muscle relaxers can lead to severe side effects. These may include:
- Allergic Reactions: Symptoms may include rash, itching, or difficulty breathing.
- Dependence: Long-term use of certain muscle relaxers, particularly carisoprodol, can lead to physical dependence.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Abrupt discontinuation after prolonged use may lead to withdrawal symptoms, such as anxiety or insomnia.
Guidelines for Using Muscle Relaxers Safely
If you’re considering using muscle relaxers, follow these guidelines to ensure safe usage:
1. Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Always talk to your doctor before starting any medication. They will assess your condition and determine if muscle are appropriate for you.
2. Follow the Prescription
Take muscle exactly as prescribed. Avoid increasing the dosage or frequency without consulting your healthcare provider.
3. Avoid Alcohol and Sedatives
Combining muscle with alcohol or other sedatives can increase the risk of severe side effects, including respiratory depression.
4. Be Aware of Drug Interactions
Inform your doctor about any other medications or supplements you’re taking. Some drugs can interact negatively with muscle .
5. Monitor Your Response
Keep track of how your body responds to the medication. If you experience concerning side effects, reach out to your healthcare provider immediately.
Natural Alternatives to Muscle Relaxers
If you prefer to avoid medications, several natural alternatives may help alleviate muscle tension. Here are some options to consider:
1. Physical Therapy
Working with a physical therapist can provide tailored exercises to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility, reducing the likelihood of spasms.
2. Massage Therapy
Massage can relieve muscle tension and promote relaxation. Consider regular sessions to maintain muscle health.
3. Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold to affected areas can reduce inflammation and relieve muscle pain. Experiment with both methods to see which works best for you.
4. Stretching and Yoga
Regular stretching or yoga practice can improve flexibility and reduce muscle tightness. Incorporating these practices into your routine may prevent future spasms.
5. Herbal Remedies
Some herbal supplements, like valerian root or chamomile, may provide mild muscle relaxant effects. Always consult a healthcare professional before trying herbal remedies.
Conclusion
Muscle relaxers can play a significant role in alleviating muscle tension and discomfort. However, it’s crucial to understand their uses, potential side effects, and safe practices. Whether you opt for prescription medication or natural alternatives, prioritize your health and well-being.
If you’re struggling with muscle pain, consult your healthcare provider to discuss the best options for your situation. By understanding muscle and their effects, you can make informed choices that enhance your quality of life. Remember, effective management of muscle tension is possible, and relief is within reach.
REFERENCE : https://www.health.com/