BOURSESSENEGAL – When exploring dietary options, many people find themselves weighing the pros and cons of vegan vs vegetarian diets. Both lifestyles promote health benefits and ethical considerations, but they differ significantly in their food choices. This guide will delve into the key distinctions between vegan and vegetarian diets, helping you understand which option may best fit your lifestyle and health goals.
What is a Vegetarian Diet?
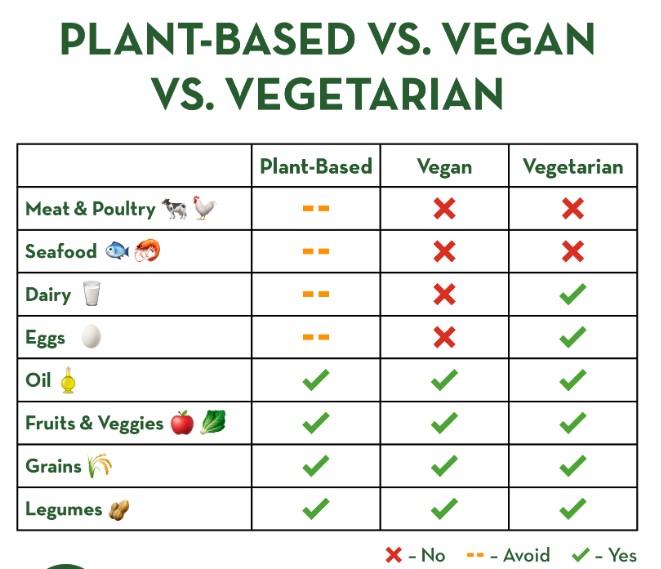
A vegetarian diet excludes meat, poultry, and fish but allows various animal products, such as eggs and dairy. Vegetarians often choose this diet for several reasons, including health benefits, ethical concerns about animal welfare, and environmental sustainability.
Types of Vegetarians
- Lacto-vegetarians: These individuals consume dairy products but avoid eggs.
- Ovo-vegetarians: They include eggs in their diet but exclude dairy.
- Lacto-ovo vegetarians: This most common type includes both dairy and eggs.
- Pescatarians: While technically not vegetarians, pescatarians consume fish along with plant-based foods, dairy, and eggs.
What is a Vegan Diet?
In contrast, a vegan diet excludes all animal products. This means no meat, dairy, eggs, or even honey. Many people choose veganism for ethical reasons, particularly concerning animal rights. Others adopt this lifestyle for health benefits, environmental concerns, or personal beliefs.
Types of Vegans
- Whole food vegans: They focus on unprocessed, whole foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and grains.
- Raw food vegans: This group eats only raw, unprocessed plant foods.
- Junk food vegans: They consume vegan versions of processed foods, which may lack nutritional value.
Key Differences Between Vegan and Vegetarian Diets
Understanding the distinctions between vegan vs vegetarian diets can help you make an informed decision.
1. Food Choices
The most apparent difference lies in food choices. Vegetarians can consume dairy and eggs, while vegans avoid all animal-derived products. This fundamental difference affects nutritional intake and the types of meals you can prepare.
2. Nutritional Aspects
Both diets can be healthy, but they require careful planning to ensure adequate nutrient intake.
Nutritional Benefits of Vegetarianism
- Protein: Eggs and dairy provide excellent protein sources.
- Calcium: Dairy products offer a rich source of calcium.
- Vitamin B12: Found in dairy and eggs, this vitamin is crucial for nerve function and blood cell formation.
Nutritional Benefits of Veganism
- Fiber: A vegan diet is typically higher in fiber, promoting better digestion.
- Antioxidants: Plant-based diets are rich in antioxidants, which combat oxidative stress.
- Lower saturated fats: Vegans tend to consume fewer saturated fats, supporting heart health.
3. Health Benefits
Both vegan and vegetarian diets offer substantial health benefits, but the impacts can vary.
Benefits of a Vegetarian Diet
- Weight management: Studies suggest that vegetarians often maintain a healthier weight.
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases: Vegetarian diets can lower the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes.
Benefits of a Vegan Diet
- Improved heart health: The absence of animal fats can lead to better cardiovascular health.
- Lower cancer risk: Some studies indicate that vegans may have a lower risk of certain cancers.
- Enhanced digestion: A diet high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains improves gut health.
4. Ethical and Environmental Considerations
Both diets stem from ethical and environmental concerns, but they differ in intensity.
Vegetarian Ethical Considerations
Vegetarians often avoid meat due to animal welfare concerns. They may still consume dairy and eggs, believing that these practices can be sustainable and humane.
Vegan Ethical Considerations
Vegans take a more stringent approach, rejecting all animal products. Their choice often reflects a commitment to preventing animal suffering and exploitation. Additionally, vegans typically emphasize environmental sustainability by reducing their carbon footprint.
Making the Right Choice: Vegan vs Vegetarian for Your Lifestyle
Choosing between vegan and vegetarian diets depends on your personal beliefs, health goals, and lifestyle. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Health Goals
If you’re looking to improve overall health, both diets can be beneficial. However, if you have specific health concerns, such as high cholesterol or obesity, a vegan diet might offer more advantages due to its lower saturated fat content.
2. Ethical Beliefs
Consider your views on animal welfare. If you feel strongly about animal rights, a vegan diet aligns more closely with those values. However, if you believe in humane treatment and sustainable practices, vegetarianism may be a suitable option.
3. Lifestyle and Convenience
A vegetarian diet may be easier to maintain if you enjoy certain dairy or egg-based dishes. Conversely, if you’re ready to embrace a plant-only lifestyle, veganism might be the way to go.
Tips for Transitioning to a Vegan or Vegetarian Diet
If you decide to make the switch, consider these helpful tips:
1. Start Slowly
Transitioning gradually can make the process easier. Begin by eliminating one food group at a time, such as red meat or dairy, to allow your body to adjust.
2. Explore New Recipes
Experimenting with new recipes can keep your meals exciting. There are countless resources online for vegan and vegetarian dishes that are both delicious and nutritious.
3. Educate Yourself
Understanding nutritional needs is crucial. Consider consulting a nutritionist or healthcare professional to ensure you’re meeting all your dietary requirements.
4. Join a Community
Finding support from like-minded individuals can make the transition smoother. Join local or online groups focused on veganism or vegetarianism for tips and encouragement.
Conclusion
In summary, the debate of vegan vs vegetarian boils down to personal choice and values. Both diets offer numerous health benefits and ethical considerations. By understanding the key differences and evaluating your own goals, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your lifestyle. Whether you choose to go fully vegan or adopt a vegetarian approach, the most important thing is to enjoy your food and feel good about your choices. Embrace the journey, and remember that every step toward a healthier diet is a positive one!
REFERENCE : https://www.health.com/