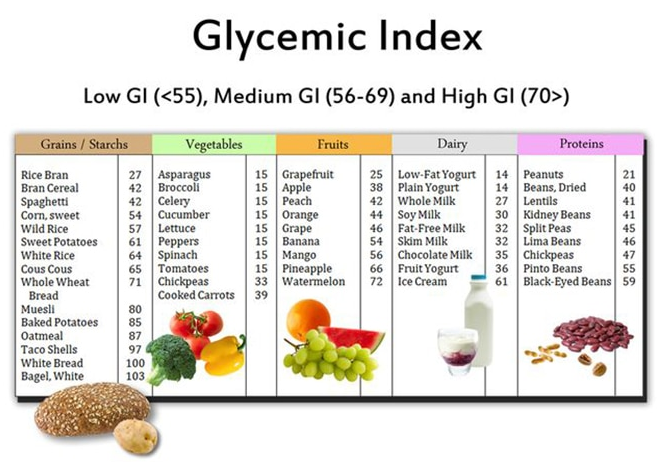
BOURSESSENEGAL – When it comes to managing your diet, the glycemic index (GI) plays a crucial role. The glycemic index measures how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels after consumption. Understanding the glycemic can help you make informed choices about what to eat, leading to improved health outcomes. This guide will provide detailed insights into the glycemic , how it affects your body, and practical tips for incorporating this knowledge into your daily life.
What is the Glycemic Index?
The glycemic index ranks carbohydrate-containing foods on a scale from 0 to 100. Foods with a high GI score (70 and above) cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, while those with a low GI score (55 and below) lead to a more gradual increase. This difference can significantly impact energy levels, hunger, and overall health.
How is the Glycemic Index Calculated?
The glycemic index is determined by measuring the blood sugar response to a specific food compared to a reference food, usually glucose or white bread. Researchers observe how much the blood sugar rises over a two-hour period after consuming the food. The resulting data helps assign a GI score, allowing individuals to make better dietary choices.
The Benefits of Low Glycemic Index Foods
Low glycemic index foods offer several health benefits:
- Stable Energy Levels: Eating foods that score low on the GI scale helps maintain consistent energy levels throughout the day. This prevents the energy crashes often associated with high GI foods.
- Better Appetite Control: Low GI foods promote feelings of fullness and satisfaction. This can lead to reduced snacking and overeating, which is beneficial for weight management.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: For individuals with diabetes or those at risk, low GI foods can help stabilize blood sugar levels, reducing the likelihood of spikes and drops.
High Glycemic Index Foods to Limit
Certain foods have a high glycemic index and should be consumed in moderation:
- White Bread: This common staple can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar.
- Sugary Snacks: Items like candy and pastries not only contain sugar but also offer little nutritional value.
- Soft Drinks: These beverages are often loaded with sugar, causing a quick increase in blood glucose levels.
How to Incorporate the Glycemic Index into Your Diet
Choosing Low Glycemic Index Foods
To harness the benefits of the glycemic index, consider integrating more low GI foods into your meals. Here are some options:
- Whole Grains: Opt for brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread instead of their white counterparts.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent low GI sources of protein and fiber.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Many fruits and non-starchy vegetables have a low GI and provide essential vitamins and minerals.
Combining Foods for a Balanced Meal
Pairing low GI foods with moderate to high GI foods can help manage blood sugar levels. For example, adding healthy fats or proteins can slow digestion and result in a more gradual increase in blood sugar. Consider these combinations:
- Whole Grain Toast with Avocado: This combination balances healthy fats with fiber, providing a satisfying meal.
- Quinoa Salad with Chickpeas and Spinach: This nutrient-packed option is low GI and full of flavor.
- Greek Yogurt with Berries: This delicious snack combines protein and low GI fruits for a satisfying treat.
Reading Food Labels
Understanding food labels can help you make better choices. Look for the following:
- Total Carbohydrates: Check the total carbs in a serving and compare them to the serving size.
- Fiber Content: Higher fiber content usually indicates a lower GI.
- Sugar Content: Be cautious of added sugars, which can raise the GI of a food.
Common Misconceptions About the Glycemic Index
The Glycemic Index is Only for Diabetics
Many people believe the glycemic is only relevant for those with diabetes. While it’s essential for blood sugar management, understanding the GI can benefit everyone. A low GI diet promotes better overall health, energy management, and weight control.
All Carbohydrates are Bad
Another common myth is that all carbohydrates should be avoided. In reality, carbohydrates are vital for providing energy. The key is choosing the right types. Focus on low GI options that provide nutritional benefits, rather than processed and refined carbohydrates.
The Glycemic Index is the Only Factor to Consider
While the glycemic index is an essential tool, it’s not the only factor to consider. Portion sizes, overall nutrient content, and meal timing all play a significant role in your dietary choices. For optimal health, adopt a holistic approach to eating.
Practical Tips for Managing Glycemic Index in Daily Life
Meal Planning and Preparation
Planning your meals ahead of time helps ensure that you incorporate low GI foods into your diet. Try these strategies:
- Create a Weekly Menu: Outline your meals and snacks for the week, focusing on low GI options.
- Batch Cooking: Prepare large portions of low GI meals that you can store and eat throughout the week.
- Smart Snacking: Keep healthy snacks, like nuts or low GI fruits, on hand to avoid high GI options when hunger strikes.
Staying Hydrated
Hydration is essential for overall health and can also affect blood sugar levels. Choose water or herbal teas instead of sugary beverages. This simple switch can significantly reduce your overall sugar intake.
Staying Informed
Educate yourself about the glycemic and its impact on health. Reading articles, attending workshops, or consulting with a nutritionist can provide valuable insights. Knowledge empowers you to make better food choices.
Conclusion: Embracing the Glycemic Index for Better Health
Understanding the glycemic index is more than just a diet trend; it’s a pathway to healthier eating and improved well-being. By choosing low GI foods, combining them thoughtfully, and planning your meals, you can maintain stable energy levels and control your appetite. Remember that balance and variety are key components of a healthy diet. With these insights, you’re well-equipped to make informed choices that support your health journey. Embrace the glycemic and transform your relationship with food for the better
REFERENCE : https://www.health.com/