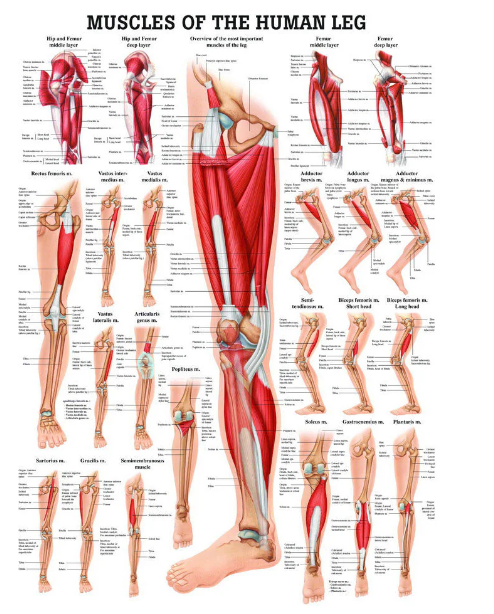
BOURSESSENEGAL – Leg muscles play a crucial role in our daily activities, from walking and running to jumping and squatting. Understanding the anatomy, function, and ways to strengthen these muscles can enhance your fitness routine and improve your overall health. In this guide, we will explore the various leg muscles, their functions, and effective training strategies to develop them.
Understanding Leg Muscles: Anatomy and Types
Leg muscles consist of several key groups, each serving unique functions. Let’s break down these muscles to understand their roles better.
Major Muscle Groups in the Legs
- Quadriceps: Located at the front of the thigh, the quadriceps group comprises four muscles: the rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius. This muscle group is essential for extending the knee and plays a vital role in activities like running and jumping.
- Hamstrings: Found at the back of the thigh, the hamstrings consist of three muscles: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus. They work to flex the knee and extend the hip, making them crucial for sprinting and other dynamic movements.
- Calves: The calf muscles, primarily the gastrocnemius and soleus, are located at the back of the lower leg. They assist in plantar flexion, which is essential for activities like walking, running, and jumping.
- Glutes: Although technically part of the hip region, the gluteal muscles (gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus) play a significant role in leg movement. They help with hip extension, abduction, and stabilization, making them vital for various physical activities.
Minor Muscle Groups
In addition to these major muscle groups, several smaller muscles contribute to leg function. These include the adductors (inner thigh muscles), tibialis anterior (front of the lower leg), and the various stabilizing muscles that support balance and movement.
The Functions of Leg Muscles
Leg muscles serve various essential functions in the body. Understanding these can help you appreciate their importance in everyday life and athletic performance.
Mobility and Movement
Leg muscles enable mobility, allowing you to perform essential activities like walking, running, and climbing stairs. The coordination between the quadriceps and hamstrings, for instance, facilitates smooth movements.
Stability and Balance
Strong leg muscles provide stability and balance, reducing the risk of falls and injuries. Well-developed muscles support the joints, helping maintain proper alignment during physical activities.
Force Generation
Leg muscles generate force, which is vital for explosive movements. Whether you’re sprinting on the track or jumping for a basketball, powerful leg muscles are key to performance.
Posture and Alignment
The muscles in your legs also support your posture. Strong glutes and hamstrings, for instance, help maintain proper alignment of the pelvis and spine, reducing strain on your back.
Training Leg Muscles: Effective Strategies
Building leg muscles requires a combination of strength training, proper technique, and consistency. Let’s explore some effective strategies to strengthen your leg muscles.
Strength Training Exercises
- Squats: Squats target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. Start with bodyweight squats, then progress to weighted squats as you gain strength. Focus on form to prevent injuries.
- Lunges: Lunges engage the same muscle groups as squats but also improve balance and coordination. Try forward, reverse, and lateral lunges to work different angles.
- Deadlifts: This compound exercise primarily targets the hamstrings and glutes. Maintaining a straight back is crucial to prevent injury. Start with lighter weights to master the technique.
- Leg Press: Using a leg press machine allows you to work on strength in a controlled manner. It’s great for isolating the quadriceps while minimizing strain on the back.
- Calf Raises: Strengthen your calves with calf raises. You can perform them standing or seated, using body weight or added resistance.
Flexibility and Mobility
Incorporating flexibility and mobility exercises into your routine can enhance overall leg strength and reduce the risk of injuries.
- Dynamic Stretching: Include dynamic stretches like leg swings and walking lunges in your warm-up routine to prepare your muscles for action.
- Static Stretching: After your workout, perform static stretches to maintain flexibility and reduce muscle tightness. Focus on hamstrings, quadriceps, and calves.
Progressive Overload
To build muscle, challenge yourself with progressive overload. Gradually increase the weights or resistance you use, the number of repetitions, or the intensity of your workouts. This technique encourages muscle growth and strength development.
Nutrition for Leg Muscle Growth
Nutrition plays a vital role in building and maintaining leg muscles. Proper fuel supports your workouts and recovery. Here are some key points to consider.
Protein Intake
Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth. Aim to consume a source of protein with each meal. Good options include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and nuts.
Carbohydrates for Energy
Carbohydrates provide the energy needed for intense workouts. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are excellent sources. Prioritize complex carbohydrates to sustain energy levels throughout your training.
Hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for optimal muscle function. Dehydration can lead to fatigue and hinder performance. Drink water throughout the day, especially before, during, and after workouts.
Common Leg Muscle Injuries and Prevention
While training leg muscles is beneficial, it can also lead to injuries if proper precautions aren’t taken. Understanding common injuries and how to prevent them is essential for maintaining a healthy workout routine.
Common Injuries
- Strains: Overstretching or overexerting leg muscles can lead to strains, particularly in the hamstrings and quadriceps. Pain, swelling, and difficulty moving are common symptoms.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of tendons, particularly in the knee and Achilles, can occur due to repetitive strain or overuse.
- Shin Splints: Pain along the shin bone often results from overuse, improper footwear, or lack of conditioning.
Prevention Strategies
- Warm-Up Properly: Always warm up before workouts to prepare your muscles for action. Dynamic stretching and light cardio can help.
- Use Proper Form: Focus on maintaining correct form during exercises to avoid unnecessary strain on your muscles and joints.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any signs of discomfort or pain. If something doesn’t feel right, don’t push through it. Rest and seek medical advice if needed.
- Incorporate Rest Days: Allow your muscles time to recover and repair by incorporating rest days into your routine. Overtraining can lead to injuries and setbacks.
Conclusion: Building Stronger Leg Muscles for a Healthier Life
Leg muscles are essential for movement, stability, and overall health. By understanding their anatomy and functions, you can appreciate the importance of training them effectively. Incorporate strength training, flexibility exercises, and proper nutrition into your routine to maximize your leg muscle potential.
Remember, consistency is key. Make leg workouts a regular part of your fitness journey, and you’ll enjoy the benefits of stronger, more resilient legs. Whether you’re an athlete or just looking to improve your everyday movement, focusing on leg muscles will enhance your quality of life. Start today and feel the difference
REFERENCE : https://www.health.com/