BOURSESSENEGAL – Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. Often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” it helps regulate calcium and phosphorus in the body, promoting strong bones and a healthy immune system. In this guide, we will explore the importance of vitamin , its sources, benefits, and the potential risks of deficiency.
What Is Vitamin D?
Vitamin is a fat-soluble vitamin that our bodies produce in response to sunlight. Unlike most vitamins, our body can synthesize it when our skin is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) rays. This unique quality makes vitamin different from many other nutrients that we must obtain solely through food.
Types of Vitamin D
There are two main types of vitamin :
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol): This form comes from plant sources and fortified foods.
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol): This type is produced in the skin when exposed to sunlight and is found in animal-based foods.
Both forms contribute to raising the levels of vitamin in your blood, but vitamin D3 is often considered more effective at increasing overall vitamin levels.
Why Is Vitamin D Important?
Vitamin D offers numerous health benefits, making it vital for overall well-being. Here are some of the key roles it plays in the body:
Bone Health
One of the most recognized functions of vitamin D is its role in bone health. It aids in calcium absorption in the gut, which is essential for maintaining bone density and preventing fractures. Without sufficient vitamin , bones can become thin and brittle, leading to conditions like osteoporosis.
Immune Function
Vitamin D supports the immune system, helping the body fight off infections. Research indicates that adequate levels of vitamin can reduce the risk of respiratory infections and may even play a role in reducing the severity of autoimmune diseases.
Mood Regulation
Some studies suggest a link between vitamin D levels and mood. Low levels may contribute to feelings of sadness or depression. Ensuring adequate vitamin intake can help promote better mental health and emotional well-being.
Heart Health
Emerging research indicates that vitamin D may support cardiovascular health. Some studies suggest that maintaining adequate vitamin levels can help regulate blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Sources of Vitamin D
Now that we understand the importance of vitamin , let’s discuss how to obtain it.
Sunlight
The most natural way to get vitamin D is through sunlight. Just 10 to 30 minutes of sun exposure several times a week can provide sufficient vitamin for most people. Factors such as skin type, time of year, and geographic location can influence how much sunlight you need.
Food Sources
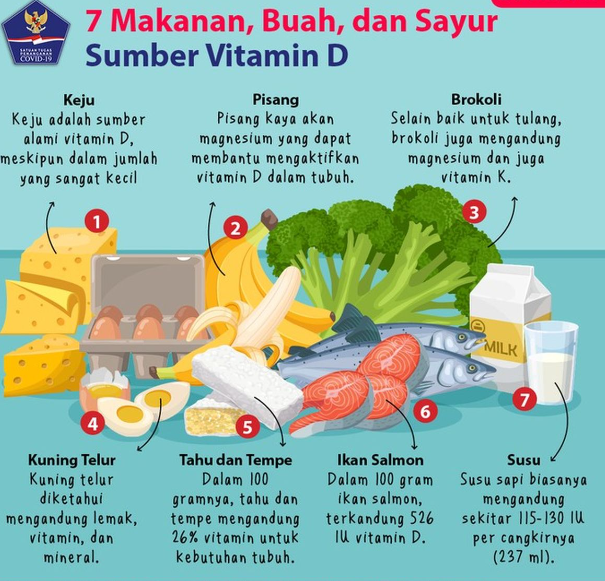
While sunlight is a primary source, certain foods also provide vitamin :
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources.
- Egg Yolks: One egg yolk contains about 37 IU of vitamin .
- Fortified Foods: Many dairy products, orange juices, and cereals are fortified with vitamin .
- Mushrooms: Some varieties exposed to UV light can be good sources of vitamin .
Supplements
For individuals who have difficulty obtaining enough vitamin D from sunlight or food, supplements can be an effective solution. Vitamin D3 is typically recommended due to its greater efficacy in raising blood levels. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement.
How Much Vitamin D Do You Need?
Determining the right amount of vitamin D can vary based on several factors, including age, sex, and overall health. The recommended dietary allowances (RDAs) for vitamin are:
- Infants (0-12 months): 400 IU (10 mcg)
- Children (1-18 years): 600 IU (15 mcg)
- Adults (19-70 years): 600 IU (15 mcg)
- Adults (71 years and older): 800 IU (20 mcg)
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women: 600 IU (15 mcg)
These recommendations may change based on individual health needs, so it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider.
Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency
Despite its importance, many people do not get enough vitamin . Common signs of deficiency include:
Fatigue and Weakness
Low vitamin levels can lead to feelings of fatigue. If you often feel tired despite a good night’s sleep, it might be worth checking your vitamin levels.
Bone Pain and Muscle Weakness
Vitamin deficiency can manifest as bone pain and muscle weakness. This occurs because the body lacks the necessary calcium to support bone health.
Increased Illness
Frequent illnesses or infections may indicate a deficiency in vitamin . Since this vitamin supports the immune system, inadequate levels can compromise your body’s defenses.
Mood Changes
Low vitamin levels may contribute to mood swings or depression. If you find yourself feeling low more often than not, consider discussing your vitamin levels with a healthcare professional.
Risks of Vitamin D Toxicity
While vitamin D is essential for health, too much can lead to toxicity. This usually occurs from excessive supplementation rather than food or sunlight. Symptoms of vitamin toxicity include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weakness and fatigue
- Confusion
- Kidney damage
If you suspect you are taking too much vitamin , consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Testing for Vitamin D Levels
If you suspect a deficiency, you can request a blood test to measure your vitamin levels. The test typically measures 25-hydroxyvitamin , the form of vitamin circulating in the bloodstream.
Understanding Your Results
Levels are typically classified as follows:
- Deficient: Less than 20 ng/mL
- Insufficient: 20-29 ng/mL
- Sufficient: 30-100 ng/mL
- Potentially Harmful: Over 100 ng/mL
Your healthcare provider can recommend steps to address any deficiencies or excesses.
Conclusion: Embrace the Benefits of Vitamin D
In conclusion, vitamin D plays a vital role in maintaining overall health. From supporting bone strength to enhancing immune function, its benefits are far-reaching. Ensuring you get enough sunlight, consuming vitamin -rich foods, and considering supplements can help maintain optimal levels.
By understanding the importance of vitamin and recognizing signs of deficiency, you can take proactive steps to improve your health. Consult with a healthcare professional to assess your needs and create a personalized plan. Embrace the sunshine vitamin, and let it shine a light on your path to better health!
REFERENCE : https://www.health.com/