BOURSESSENEGAL – An anti-inflammatory diet can significantly impact your health and well-being. With chronic inflammation linked to numerous diseases, understanding how to combat it through diet is crucial. This guide will explore what an anti-inflammatory diet entails, its benefits, key foods to include, and practical tips for adopting this lifestyle.
What Is an Anti-Inflammatory Diet?
An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on consuming foods that reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation can contribute to conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and even cancer. By prioritizing whole, nutrient-dense foods, you can support your body’s natural ability to fight inflammation.
The Connection Between Diet and Inflammation
What you eat plays a significant role in your body’s inflammatory processes. Foods high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats can trigger inflammation. Conversely, certain foods can help combat this process. Thus, an anti-inflammatory diet centers around the right choices.
Benefits of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
1. Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
Research indicates that adopting an anti-inflammatory diet can lower your risk of chronic diseases. Conditions like heart disease, obesity, and diabetes often stem from chronic inflammation. By reducing inflammation through diet, you protect your health in the long run.
2. Improved Mental Health
Emerging studies suggest a connection between inflammation and mental health. An anti-inflammatory diet may help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins support brain health and overall mood.
3. Enhanced Gut Health
Your gut health significantly influences inflammation levels. An anti-inflammatory diet promotes a healthy gut microbiome, which can reduce inflammation and improve digestion. Including fiber-rich foods supports beneficial gut bacteria.
Key Components of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
1. Whole Foods
Prioritizing whole, unprocessed foods is essential. These foods contain vital nutrients and antioxidants that combat inflammation. Focus on fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
2. Healthy Fats
Incorporate healthy fats into your meals. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds, play a crucial role in reducing inflammation. Additionally, olive oil is an excellent source of monounsaturated fats, known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
3. Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. Include colorful fruits and vegetables like berries, leafy greens, and sweet potatoes. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients that support overall health.
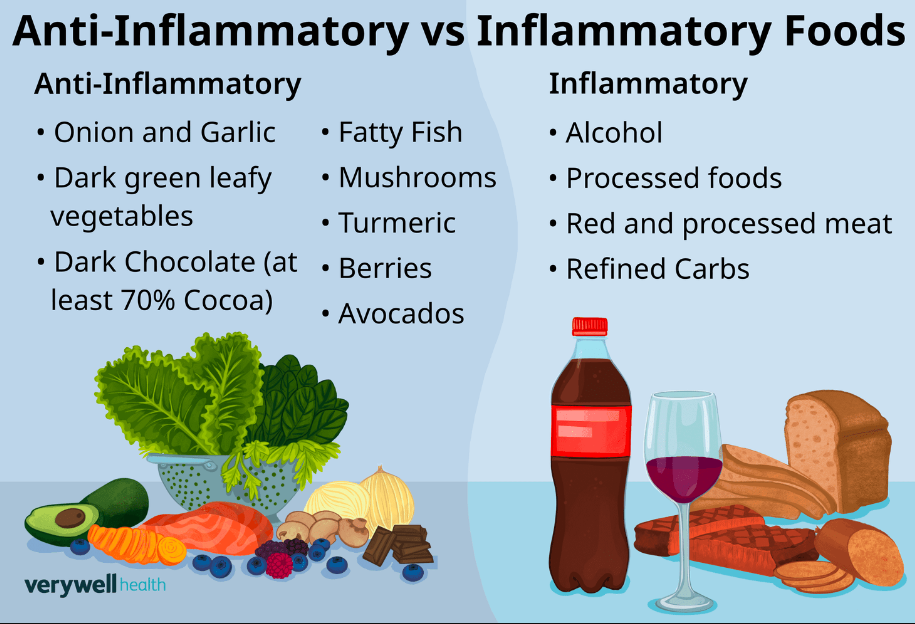
Foods to Include in an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
1. Fruits and Vegetables
Aim to fill your plate with a variety of fruits and vegetables. Berries, cherries, spinach, kale, and broccoli are excellent choices. They contain high levels of antioxidants and phytochemicals that reduce inflammation.
2. Whole Grains
Choose whole grains over refined grains. Options like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread provide fiber and essential nutrients. They help maintain stable blood sugar levels, which can reduce inflammation.
3. Lean Proteins
Incorporate lean protein sources such as chicken, turkey, tofu, and legumes. These foods support muscle health without contributing to inflammation. Fatty fish like salmon and sardines also provide healthy omega-3 fats.
4. Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are nutrient powerhouses. Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds offer healthy fats, fiber, and protein. They can help reduce inflammation while keeping you full and satisfied.
5. Herbs and Spices
Don’t overlook the power of herbs and spices. Turmeric, ginger, garlic, and cinnamon are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Adding these ingredients to your meals can boost flavor and health benefits.
Foods to Avoid
1. Processed Foods
Steer clear of processed and packaged foods. These items often contain added sugars, unhealthy fats, and preservatives that can trigger inflammation. Opt for fresh, whole foods whenever possible.
2. Refined Carbohydrates
Foods like white bread, pastries, and sugary cereals can spike blood sugar levels, leading to inflammation. Instead, choose whole grains that provide fiber and nutrients.
3. Sugary Beverages
Limit your intake of sugary drinks such as sodas and fruit juices. These beverages can contribute to weight gain and inflammation. Opt for water, herbal teas, or infused water with fresh fruits.
4. Trans Fats
Avoid trans fats commonly found in fried foods, baked goods, and margarine. These unhealthy fats increase inflammation and are linked to heart disease. Check food labels and choose products free of trans fats.
Tips for Adopting an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
1. Plan Your Meals
Planning your meals can simplify your transition to an anti-inflammatory diet. Set aside time each week to create a menu and grocery list. This practice helps you stay on track and makes healthy eating more accessible.
2. Cook at Home
Cooking at home allows you to control the ingredients in your meals. Experiment with new recipes that emphasize whole, anti-inflammatory foods. Preparing meals from scratch can be fun and rewarding.
3. Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to how your body reacts to certain foods. Everyone’s body is different, and some foods may trigger inflammation in specific individuals. Keep a food diary to identify patterns and adjust your diet accordingly.
4. Stay Hydrated
Hydration is essential for overall health. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support your body’s functions. Herbal teas and infused water can also contribute to your daily fluid intake.
5. Be Patient
Transitioning to an anti-inflammatory diet takes time. Be patient with yourself and make gradual changes. Focus on incorporating more anti-inflammatory foods rather than eliminating everything at once.
Conclusion: Embrace an Anti-Inflammatory Lifestyle
An anti-inflammatory diet offers numerous health benefits, from reducing chronic disease risk to improving mental well-being. By prioritizing whole foods, healthy fats, and antioxidant-rich options, you can create a diet that supports your body’s natural defenses against inflammation.
Remember, it’s not just about what you avoid but also about what you embrace. Make small, sustainable changes that lead to a healthier lifestyle. As you embark on this journey, celebrate each step towards better health and well-being. Your body will thank you!
REFERENCE : https://www.health.com/