BOURSESSENEGAL – Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It causes red, flaky patches on the skin that can be itchy and painful. If you or someone you know is struggling with , understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower you to manage this condition effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into everything you need to know about , including lifestyle changes that can help.
What Is Psoriasis?
Definition and Overview
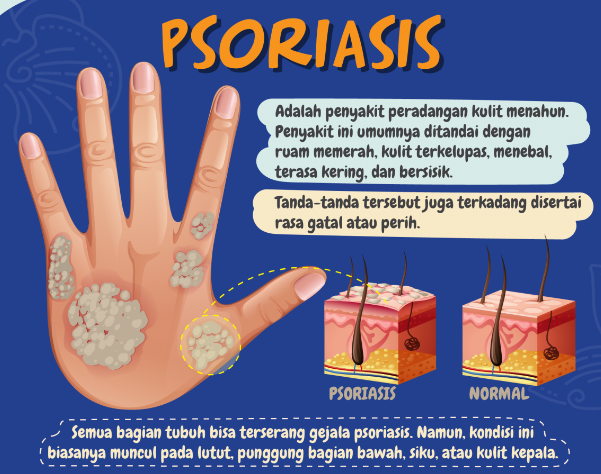
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that leads to the rapid growth of skin cells. This overproduction results in thick, scaly patches on the skin, commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. While is not contagious, it can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Several types of psoriasis exist, each with distinct features:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common form, characterized by raised, red patches covered with thick, silvery scales.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Often appears as small, drop-shaped lesions, typically triggered by infections such as strep throat.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Manifests as bright red, shiny lesions in skin folds, such as under the breasts or in the groin.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Characterized by white pustules (blisters) surrounded by red skin. This form can occur on any part of the body.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A rare and severe form that can cover large areas of the body with a red, peeling rash.
Causes of Psoriasis
1. Genetic Factors
Research shows that psoriasis often runs in families. If someone in your family has , your risk of developing it increases. However, having a family history doesn’t guarantee you will get the condition.
2. Immune System Dysfunction
Psoriasis is primarily an autoimmune disorder. In individuals with, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing them to multiply rapidly. This accelerated growth leads to the characteristic patches associated with the condition.
3. Environmental Triggers
Certain environmental factors can trigger psoriasis or worsen existing symptoms. Common triggers include:
- Stress: High stress levels can exacerbate symptoms.
- Infections: Illnesses, particularly streptococcal infections, can lead to flare-ups.
- Skin Injuries: Cuts, scrapes, or sunburns can trigger new lesions.
- Weather: Cold, dry weather may worsen symptoms, while warm, sunny conditions can sometimes improve them.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
1. Skin Changes
The most recognizable symptoms of psoriasis are the skin lesions. These patches can vary in size and can appear anywhere on the body. They may be itchy or painful and often have a defined edge.
2. Nail Changes
Psoriasis can also affect the nails, leading to pitting, abnormal nail growth, or discoloration. In severe cases, nails may become loose and separate from the nail bed.
3. Joint Pain
Some individuals with psoriasis may develop psoriatic arthritis, a condition that causes inflammation and pain in the joints. Symptoms can include swelling, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
1. Physical Examination
To diagnose psoriasis, healthcare providers typically perform a physical examination of the skin, nails, and scalp. They look for characteristic signs of the condition.
2. Medical History
Your doctor will also take a medical history, including family history, to understand the likelihood of psoriasis. Discussing previous skin conditions or treatments can help guide the diagnosis.
3. Biopsy (if necessary)
In some cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary. A small sample of skin is taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other skin disorders.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
1. Topical Treatments
For mild to moderate psoriasis, topical treatments can be effective. These include:
- Corticosteroids: Help reduce inflammation and slow skin cell turnover.
- Vitamin D Analogues: Slow down skin cell growth and can be used alongside other treatments.
- Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, these can help reduce scaling.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Help reduce inflammation and plaque buildup, especially in sensitive areas.
2. Phototherapy
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. This treatment can be effective for moderate to severe psoriasis. It helps slow the growth of skin cells and reduces inflammation.
3. Systemic Treatments
For more severe cases, systemic treatments may be necessary. These medications affect the entire body and include:
- Biologics: Target specific parts of the immune system and can significantly improve symptoms.
- Methotrexate: A traditional systemic medication that slows down cell growth and suppresses the immune system.
- Oral Retinoids: Can help reduce skin cell production.
4. Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can complement medical treatments:
- Moisturizing: Keeping the skin well-hydrated can reduce dryness and irritation.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help manage symptoms. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, and antioxidants in fruits and vegetables are particularly beneficial.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels.
Coping with Psoriasis
1. Support Groups
Connecting with others who understand your experience can provide emotional support. Consider joining a support group for individuals with to share experiences and coping strategies.
2. Educating Yourself
Understanding your condition empowers you to take control. Read books, attend workshops, and explore reputable online resources about to stay informed.
3. Open Communication with Healthcare Providers
Maintain open communication with your healthcare team. Discuss your symptoms, treatment preferences, and any side effects you experience. This collaboration is essential for effective management.
Conclusion: Living with Psoriasis
Psoriasis can be a challenging condition, affecting both physical health and emotional well-being. However, with the right understanding and treatment, you can manage your symptoms effectively. By exploring available treatment options and making lifestyle changes, you can lead a fulfilling life despite the challenges of . Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and support is available.
Take the time to educate yourself about psoriasis, seek support, and explore different treatment strategies. Empower yourself with knowledge, and don’t hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals who can guide you in managing this condition.
This guide provides a thorough understanding of psoriasis while effectively engaging the reader. If you have specific requests or need further adjustments, feel free to let me know
REFERENCE : https://www.health.com/