PUBLIC HEALTH – When your doctor tells you that your monocytes are high, it may raise concerns. Monocytes are a type of white blood cell that play a crucial role in your immune system, helping your body fight infections and clear dead cells. But what happens when these cells are elevated? A high monocyte count, also known as monocytosis, can indicate an underlying health issue. In this article, we’ll explore the potential causes, symptoms, and treatments for high monocytes and what you need to know about this condition.
What Are Monocytes?
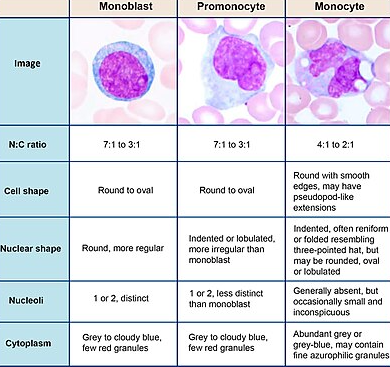
Monocytes are a type of white blood cell produced by the bone marrow. They circulate in the bloodstream for about one to three days before moving to tissues in your body, where they become macrophages or dendritic cells. These cells are essential for fighting infections, digesting dead cells, and playing a role in immune responses.
Monocytes make up approximately 2–8% of the total white blood cell count. When your body faces an infection or inflammation, your bone marrow may produce more monocytes, increasing their numbers in your blood. Although monocytes play a vital role in immune defense, an elevated count could also signal a medical condition that needs attention.
What Does It Mean When Monocytes Are High?
A high monocyte count, or monocytosis, occurs when the number of monocytes in your blood exceeds the normal range. It’s essential to understand that monocytosis is not a disease itself but a symptom that points to an underlying health issue. Your healthcare provider will assess your overall symptoms and other blood test results to identify the cause.
Causes of High Monocytes
There are several conditions that could lead to high monocytes. These can range from infections to chronic conditions, and even certain types of cancer. Let’s explore some common causes of monocytes high:
1. Infections
Infections are one of the most common reasons for elevated monocytes. As part of your immune system, monocytes increase in number to help combat bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. Some of the infections that can trigger high monocyte levels include:
- Tuberculosis: A bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body.
- Bacterial infections: Any bacterial infection, including sepsis or endocarditis, can cause an increase in monocytes.
- Viral infections: Viruses like HIV, hepatitis, and mononucleosis (caused by the Epstein-Barr virus) can lead to elevated monocytes.
2. Chronic Inflammatory Conditions
Monocytes also rise in response to chronic inflammation. Conditions that cause persistent inflammation include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune disorder that causes joint inflammation and can lead to long-term high monocyte levels.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): An autoimmune disease that affects various organs, leading to inflammation and tissue damage.
3. Blood Disorders and Cancers
Certain types of blood disorders and cancers can cause an increase in monocytes:
- Leukemia: A type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, leading to abnormal production of white blood cells, including monocytes.
- Myeloproliferative disorders: Conditions where the bone marrow produces too many blood cells, including monocytes.
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma: A cancer of the lymphatic system that can lead to changes in white blood cell levels.
4. Recovery from an Infection or Trauma
After an infection or trauma, your body may produce more monocytes to help with the healing process. This can cause temporary high monocytes, especially in the recovery phase after surgery or a significant injury.
5. Other Causes
Other less common causes of high monocytes can include:
- Chronic stress: Prolonged stress can activate the immune system, leading to elevated monocyte levels.
- Obesity: Obesity has been associated with inflammation, which can lead to a higher monocyte count.
- Certain medications: Some drugs, like corticosteroids, may lead to elevated monocyte levels as a side effect.
Symptoms of High Monocytes
High monocytes themselves may not cause symptoms. However, the underlying condition causing the elevated monocytes can lead to noticeable signs. These may include:
- Fatigue: Feeling tired all the time, which is common in inflammatory and autoimmune conditions.
- Fever: High monocytes can indicate an ongoing infection, which may be accompanied by fever.
- Pain or swelling: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or infections may cause pain or swelling in the affected areas.
- Unexplained weight loss: Weight loss can occur in some cancers or chronic infections.
- Lymph node swelling: Swollen lymph nodes may be a sign of an infection or lymphatic cancer like lymphoma.
If you experience any of these symptoms along with high monocytes, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause.
How Is High Monocytes Diagnosed?
To diagnose monocytes high, a blood test called a complete blood count (CBC) with a differential is typically performed. This test measures the number of different types of blood cells, including monocytes. If the results show a higher than normal monocyte count, your doctor may recommend additional tests to identify the cause.
These additional tests could include:
- Blood cultures to check for infections.
- X-rays or CT scans to look for signs of infection or cancer.
- Bone marrow biopsy if a blood disorder like leukemia is suspected.
- Autoimmune panels to test for conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment for High Monocytes
Treatment for high monocytes depends on the underlying cause. For instance:
- If the elevated monocytes are due to an infection, antibiotics or antivirals may be prescribed.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs or immunosuppressive treatments may be necessary for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
- Cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation, may be required for blood cancers or lymphoma.
- In cases of stress-related increases, lifestyle changes like stress management, exercise, and a balanced diet can help normalize monocyte levels.
When to See a Doctor
If you have high monocytes, it’s important to work with your healthcare provider to identify the cause. If you experience persistent or unexplained symptoms like fever, pain, fatigue, or unexplained weight loss, consult a doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and help manage the condition effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, high monocytes can be a sign of an underlying health condition, ranging from infections and chronic inflammation to blood disorders or cancer. While an elevated monocyte count is not a disease itself, it is a useful marker that helps healthcare providers diagnose and treat various medical issues. If you’re concerned about your monocyte levels or experiencing symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. By understanding the causes and treatment options for high monocytes, you can take proactive steps toward improving your health and well-being.