PUBLIC HEALTH – When it comes to eye color, there’s a world of variation that goes beyond the typical shades of brown, blue, or green. Two unique eye colors that often catch people’s attention are central heterochromia and hazel eyes. While both are beautiful and striking, they have distinct characteristics that set them apart. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the central heterochromia vs hazel debate, explaining what each eye color is, how they’re formed, and how to tell them apart.
If you’ve ever wondered why your eyes look different from someone else’s, or if you’ve noticed that the color of your eyes seems to change with the light, understanding the science behind these eye colors can shed light on these intriguing differences.
What is Central Heterochromia?
A Rare Eye Condition
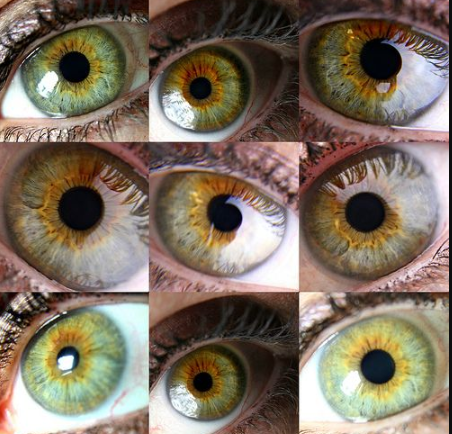
Central heterochromia refers to a condition where the eyes are two different colors, but it’s more specific than just having two different-colored eyes. In central heterochromia, the outer part of the iris (the colored portion of the eye) is one color, while the inner part, or the area around the pupil, is a different color.
This condition is most often seen in people with one iris that has two different colors, but it can also be present in people with two separate irises of different colors. It’s considered rare, but not overly uncommon. Central heterochromia can occur in one or both eyes, meaning you could have one eye with a different-colored ring around the pupil compared to the outer iris.
Causes of Central Heterochromia
The main cause of central heterochromia is genetic inheritance. It occurs when there is a genetic variation that affects the pigmentation of the iris. In most cases, central heterochromia is inherited, but it can also develop as a result of trauma, injury, or certain medical conditions, such as Horner’s syndrome or Waardenburg syndrome.
While central heterochromia doesn’t usually cause any vision problems, it can be a sign of an underlying health condition, so if there are sudden changes in eye color or associated symptoms like vision changes or pain, it’s always a good idea to see a doctor.
Unique Features of Central Heterochromia
- Distinct Color Contrast: The most striking feature of central heterochromia is the contrast between the two colors. Often, the outer iris will be one color (like green or brown), and the inner ring around the pupil will be a different shade (like gold or blue). This creates a stunning effect that can make the eyes appear multi-colored.
- Fluctuating Color: The color of the iris may seem to change depending on the lighting and the clothing you wear. For instance, a person with central heterochromia may notice that their eyes look more green in one light, but shift to gold or brown in another. This is because the different pigments in the iris can reflect light in different ways.
- Rare and Unique: Though central heterochromia is rare, it’s also an eye condition that stands out. It’s an eye feature that many people find captivating, and it adds a layer of uniqueness to the individual.
What Are Hazel Eyes?
A Complex and Fascinating Eye Color
Unlike central heterochromia, hazel eyes are a single color but with an intricate blend of green, brown, and gold hues. The beauty of hazel eyes lies in their complexity. They often appear to change color depending on the lighting or the color of the clothing worn, which is why many people describe hazel eyes as having “multi-colored” characteristics.
Causes of Hazel Eyes
Hazel eyes are a result of how light interacts with the melanin in the iris. The iris contains two layers of pigment, and the amount of melanin in each layer determines the eye color. In people with hazel eyes, the outer layer has a relatively small amount of melanin, while the inner layer has a higher amount. This unique balance allows light to scatter in a way that creates the signature hazel effect.
In addition to genetics, environmental factors such as lighting and the color of clothing can affect how hazel eyes appear. Hazel eyes are often inherited in families and are more common in people of Caucasian and Middle Eastern descent.
Unique Features of Hazel Eyes
- Shifting Color: One of the most notable characteristics of hazel eyes is their ability to change color. Depending on the lighting, hazel eyes can appear to be more green, brown, or golden. This is due to the light reflecting off the melanin in the iris, which gives it a dynamic quality.
- Irises with Multiple Tones: Hazel eyes often contain a mixture of different tones. You may notice small flecks of gold, brown, or green within the iris, which can make hazel eyes appear to shimmer or sparkle when exposed to the right light.
- Common Yet Beautiful: While not as rare as central heterochromia, hazel eyes are still considered unique and desirable due to their striking and ever-changing appearance.
Central Heterochromia vs Hazel: Key Differences
1. Eye Color Composition
- Central Heterochromia: Involves two distinct colors in the eye, typically a different color in the outer iris and around the pupil. This creates a distinct contrast between the inner and outer portions of the iris.
- Hazel Eyes: Have a blend of colors, primarily green, brown, and gold, within the same iris. The color appears to shift and change based on light conditions but is not divided into two distinct regions like in central heterochromia.
2. Color Shifting Properties
- Central Heterochromia: The color contrast is usually fixed, with the outer and inner parts of the iris remaining constant in color.
- Hazel Eyes: The color of hazel eyes can appear to shift throughout the day or depending on clothing and lighting, creating a more dynamic appearance.
3. Rarity and Uniqueness
- Central Heterochromia: Is rare and often considered an unusual and captivating eye feature.
- Hazel Eyes: While more common than central heterochromia, they are still regarded as beautiful and intriguing, with their multi-tonal hues.
4. Health Implications
- Central Heterochromia: Is usually harmless, though it can sometimes be associated with underlying medical conditions, so it’s important to monitor any sudden changes.
- Hazel Eyes: Have no health implications related to their color; they are a natural variation of eye pigmentation.
Which Is More Common: Central Heterochromia or Hazel Eyes?
While both eye colors are unique, hazel eyes are far more common than central heterochromia. Central heterochromia is considered a rare phenomenon, particularly in its full expression (two eyes with two different colors or one eye with two distinct shades). On the other hand, hazel eyes are a widespread natural variation that occurs in many individuals, particularly in those with European or Middle Eastern ancestry.
Conclusion: Embracing Your Eye Color
Whether you have central heterochromia or hazel eyes, both eye colors are beautiful and fascinating in their own way. Central heterochromia vs hazel may seem like a simple comparison, but when you consider the genetics, light effects, and personal experience of each, both types of eye colors are unique gifts.
By understanding the science behind the colors and how they form, we can appreciate the diversity of eye color and the subtle ways in which light interacts with our irises. So, whether you have a rare set of heterochromatic eyes or a stunning hazel gaze, each one is a natural wonder that enhances your individuality.