BOURSESSENEGAL – Chronic gastritis is a common condition that affects many individuals worldwide. This ongoing inflammation of the stomach lining can lead to discomfort and various digestive issues. If you’re looking for insights on chronic , its causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options, you’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with the information you need to understand and manage this condition.
What is Chronic Gastritis?
Definition and Overview
Chronic gastritis refers to the long-term inflammation of the stomach lining. Unlike acute gastritis, which occurs suddenly and typically lasts a short time, chronic develops gradually. This condition can persist for months or even years, leading to significant discomfort and potential complications if left untreated.
Types of Chronic Gastritis
There are several types of chronic gastritis, each with different causes and characteristics:
- Chronic Non-atrophic Gastritis: Often linked to Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection, this type causes inflammation without significant damage to the stomach lining.
- Chronic Atrophic Gastritis: This condition involves the loss of gastric glandular cells, which can lead to a decrease in stomach acid production. It often results from long-term inflammation or autoimmune disorders.
- Chemical Gastritis: Caused by irritants such as bile reflux, excessive alcohol consumption, or certain medications, this type can damage the stomach lining over time.
Understanding these variations can help identify the specific type affecting you and guide appropriate treatment.
Causes of Chronic Gastritis
1. Helicobacter Pylori Infection
H. pylori is a type of bacteria that can infect the stomach lining. This infection is one of the leading causes of chronic . It can lead to inflammation and increase the risk of developing ulcers and gastric cancer if not treated.
2. Long-term Use of Medications
Certain medications, particularly nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can irritate the stomach lining. Regular use of these drugs can lead to chronic inflammation, resulting in gastritis.
3. Autoimmune Disorders
In autoimmune chronic , the immune system mistakenly attacks the stomach lining. This can lead to inflammation and a loss of stomach cells, decreasing acid production and affecting digestion.
4. Alcohol and Tobacco Use
Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking can irritate the stomach lining, contributing to chronic . Both substances can lead to inflammation and damage the protective mucus layer.
5. Stress
While stress alone may not directly cause chronic it can exacerbate existing symptoms. Stress can increase stomach acid production and worsen inflammation.
Symptoms of Chronic Gastritis
1. Abdominal Pain and Discomfort
One of the most common symptoms of chronic is abdominal pain. This discomfort may manifest as a burning sensation or aching in the upper abdomen. The pain often fluctuates in intensity.
2. Nausea and Vomiting
Individuals with chronic may experience nausea, which can sometimes lead to vomiting. This symptom can be particularly distressing and may occur after eating.
3. Loss of Appetite
Chronic inflammation in the stomach can lead to a reduced appetite. Many people with this condition find it challenging to eat, leading to unintentional weight loss.
4. Bloating and Indigestion
Bloating, a feeling of fullness, and indigestion are common symptoms. These digestive issues can occur after meals and contribute to overall discomfort.
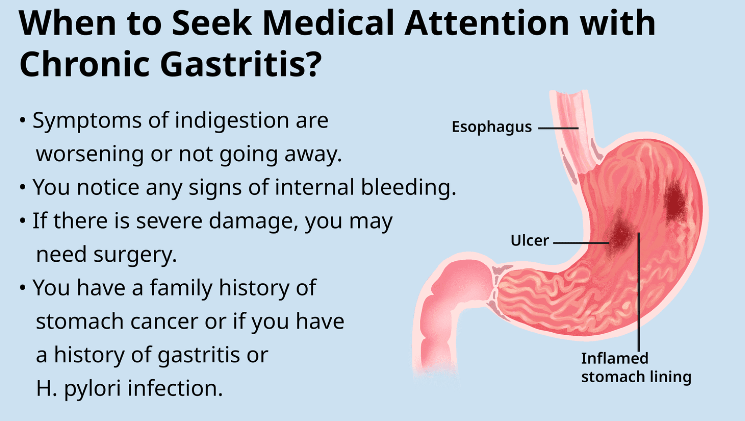
5. Dark or Tarry Stools
In some cases, chronic can lead to bleeding in the stomach, resulting in dark or tarry stools. This symptom requires immediate medical attention.
Diagnosing Chronic Gastritis
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
To diagnose chronic gastritis, a healthcare provider will start by taking a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination. Discussing your symptoms, medication use, and lifestyle habits is crucial.
2. Endoscopy
An upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy may be necessary to visualize the stomach lining directly. During this procedure, a thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth to examine the stomach and collect tissue samples if needed.
3. Lab Tests
Your doctor may order lab tests to check for H. pylori infection or assess levels of stomach acid. Blood tests can also help determine if you have anemia or other related conditions.
Treatment Options for Chronic Gastritis
1. Medications
Several medications can help manage chronic gastritis, including:
- Antacids: These over-the-counter medications can neutralize stomach acid and relieve symptoms.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): These drugs reduce acid production in the stomach, promoting healing of the gastric lining.
- Antibiotics: If H. pylori infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed to eradicate the bacteria.
2. Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve symptoms:
- Dietary Modifications: Avoiding irritants such as spicy foods, acidic foods, and alcohol can help reduce inflammation. Opt for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress levels, which may alleviate symptoms.
3. Avoiding Irritants
If you use medications like NSAIDs regularly, discuss alternatives with your healthcare provider. Limiting or avoiding alcohol and quitting smoking can also promote healing of the stomach lining.
4. Regular Monitoring
If you have chronic gastritis, regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential. Monitoring your condition allows for timely adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
Complications of Chronic Gastritis
1. Stomach Ulcers
Untreated chronic gastritis can lead to the development of stomach ulcers. These painful sores can cause significant discomfort and may result in bleeding.
2. Gastric Cancer
In some cases, chronic atrophic gastritis can increase the risk of gastric cancer. Regular monitoring and early intervention are crucial to reduce this risk.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies
Chronic inflammation can affect nutrient absorption, leading to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals. This can result in conditions such as anemia.
Conclusion: Managing Chronic Gastritis
Chronic gastritis can significantly impact your quality of life, but understanding the condition empowers you to manage it effectively. By recognizing the causes and symptoms, seeking timely treatment, and making lifestyle changes, you can alleviate discomfort and promote healing.
If you suspect you have chronic gastritis, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and tailored treatment plan. Don’t let this condition control your life; take proactive steps toward better digestive health.
With the right approach, you can navigate the challenges of chronic and enjoy a healthier, more comfortable life.
This guide provides a detailed overview of chronic gastritis while effectively engaging the reader. If you need any adjustments or further information, feel free to let me know
REFERENCE : https://www.health.com/