BOURSESSENEGAL – Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious condition that can arise from uncontrolled diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes. Many people wonder, “how long does it take to die from diabetic ketoacidosis?” Understanding DKA, its causes, symptoms, and treatment can help you recognize its severity and the importance of prompt medical attention. Let’s dive into this crucial topic.
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones, which are acids that accumulate when the body breaks down fat for energy instead of glucose. This situation usually happens when there isn’t enough insulin to allow glucose to enter cells. Consequently, the body turns to fat as an alternative fuel source, leading to an increase in ketones in the blood.
Why DKA Happens
DKA primarily affects individuals with diabetes. Factors that can trigger this condition include:
- Infection: Infections can cause stress in the body, leading to higher blood sugar levels.
- Insulin omission: Skipping insulin doses can result in elevated blood glucose levels.
- Illness or injury: Physical stress from illness or injury can also prompt DKA.
- Poor management: Inadequate diabetes management can lead to elevated blood sugars and subsequent ketoacidosis.
Understanding these triggers is vital for prevention and timely intervention.
Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
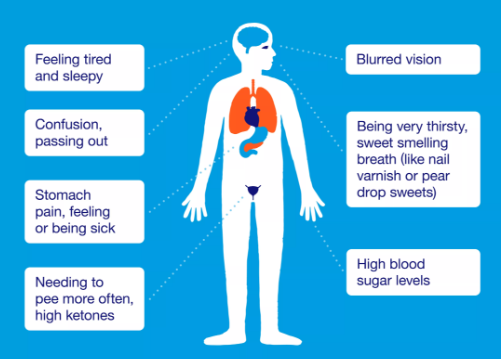
Recognizing the symptoms of DKA is critical for early diagnosis and treatment. Common signs include:
- Excessive thirst: A significant increase in thirst, often coupled with frequent urination.
- Nausea and vomiting: Digestive issues may arise as the body struggles with the metabolic changes.
- Abdominal pain: Many individuals experience discomfort in the stomach area.
- Shortness of breath: As ketone levels rise, individuals may find it difficult to breathe normally.
- Confusion or altered consciousness: High levels of ketones can affect mental clarity.
If you or someone you know exhibits these symptoms, seek medical help immediately.
How Long Does It Take to Die from Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
Timeframe of DKA Progression
When considering how long does it take to die from diabetic ketoacidosis, it’s important to note that the timeframe varies. Without treatment, DKA can lead to severe complications and can be fatal within 24 to 72 hours. However, the actual time depends on several factors, including:
- Severity of the condition: The higher the levels of ketones and glucose, the quicker the body can deteriorate.
- Individual health status: A person’s overall health and existing medical conditions influence the progression of DKA.
- Access to medical care: Timely treatment can significantly alter outcomes.
Complications from Untreated DKA
Without prompt intervention, DKA can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Coma: Severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalances can cause unconsciousness.
- Organ failure: Prolonged acidosis can result in the failure of vital organs, such as the kidneys and heart.
- Death: Ultimately, untreated DKA can lead to fatal outcomes.
Importance of Timely Treatment
Understanding that DKA can progress rapidly emphasizes the importance of seeking medical care at the first signs of symptoms. Early intervention can dramatically improve the prognosis.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Medical Intervention
If DKA occurs, immediate medical treatment is crucial. Treatment generally includes:
- Fluid Replacement: Administering intravenous (IV) fluids helps restore hydration and dilute ketones in the blood.
- Electrolyte Management: Medical professionals monitor and replace electrolytes, like potassium, which can become dangerously low during DKA.
- Insulin Therapy: Administering insulin helps lower blood sugar levels and halt the production of ketones.
Monitoring and Recovery
During treatment, healthcare providers closely monitor vital signs, blood sugar levels, and ketone levels. Most patients see improvement within a few hours of treatment, but recovery can take days, depending on the severity of DKA.
Prevention of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Managing Diabetes Effectively
Preventing DKA starts with effective diabetes management. Here are some tips:
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly check your blood sugar to ensure it remains within target ranges.
- Follow Treatment Plans: Stick to prescribed insulin regimens and adjust as needed based on factors like illness or stress.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids can help prevent dehydration, which is crucial in reducing the risk of DKA.
- Recognize Symptoms Early: Understanding the warning signs of DKA can prompt early intervention.
Lifestyle Changes
Incorporating lifestyle changes can also aid in prevention. Consider:
- Healthy Eating: A balanced diet helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of complications.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress through mindfulness or relaxation techniques can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
When to Seek Medical Help
Recognizing Emergency Signs
If you experience symptoms of DKA or notice someone else exhibiting these signs, don’t hesitate to seek medical help. Early intervention saves lives.
Regular Check-Ups
Routine check-ups with healthcare providers can help manage diabetes effectively and minimize the risk of DKA. These appointments allow for medication adjustments and educational resources that empower patients.
Conclusion: The Critical Nature of Understanding DKA
Diabetic ketoacidosis poses a serious threat to individuals with diabetes. Knowing how long does it take to die from diabetic ketoacidosis underscores the urgency of addressing this condition. While DKA can progress rapidly, timely treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for DKA, you can better manage your health or support others in navigating this challenging condition. Remember, effective diabetes management and awareness are your best defenses against diabetic ketoacidosis. Stay informed, stay proactive, and seek help whenever necessary. Your health depends on it.
REFERENCE : https://www.health.com/