BOURSESSENEGAL – Gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted infection (STI), affects millions of people each year. Recognizing gonorrhea symptoms early is crucial for prompt treatment and preventing complications. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the signs of gonorrhea, how it spreads, potential complications, and the importance of seeking medical help. Understanding these aspects can empower you to take control of your sexual health.
What is Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It primarily spreads through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. While it affects both men and women, symptoms may manifest differently based on gender.
How Gonorrhea Spreads
Gonorrhea spreads through bodily fluids during sexual activities. It can also be passed from mother to child during childbirth. Understanding how it transmits can help reduce the risk of infection.
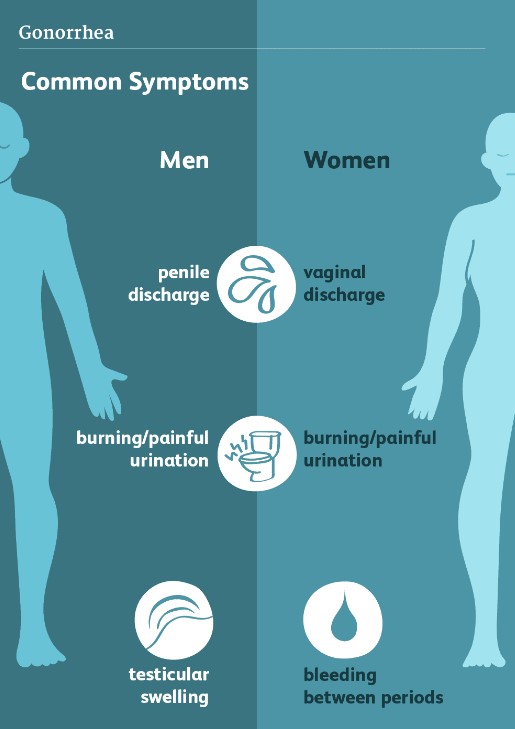
Common Gonorrhea Symptoms
Recognizing gonorrhea symptoms early is essential for effective treatment. Symptoms may vary between genders, and some individuals may be asymptomatic.
Symptoms in Men
Men typically experience noticeable symptoms within a few days of infection. Common signs include:
- Painful Urination: A burning sensation during urination is a common complaint.
- Discharge: A thick, yellowish or greenish discharge from the penis may occur.
- Swollen Testicles: Inflammation and pain in one or both testicles can happen.
- Sore Throat: If gonorrhea affects the throat, soreness may occur after oral sex.
Recognizing Symptoms Early
If you notice any of these symptoms, don’t wait. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications.
Symptoms in Women
Women often experience milder symptoms, which can make diagnosis challenging. Common gonorrhea symptoms in women include:
- Painful Urination: Like men, women may also feel pain when urinating.
- Increased Vaginal Discharge: Changes in discharge consistency or color can indicate infection.
- Pelvic Pain: Some women may experience discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen.
- Irregular Bleeding: This could include spotting between periods or heavy menstrual bleeding.
The Challenge of Asymptomatic Cases
Many women may not show symptoms at all, making it crucial to get tested regularly if you are sexually active.
Symptoms in Both Genders
Both men and women can experience symptoms in the rectal and throat areas:
- Rectal Symptoms: These may include itching, discharge, and discomfort.
- Throat Symptoms: Gonorrhea in the throat can cause soreness and difficulty swallowing.
Potential Complications of Untreated Gonorrhea
Ignoring gonorrhea symptoms can lead to serious health complications. Both men and women face risks, which is why prompt treatment is essential.
Complications in Men
If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to:
- Epididymitis: An infection of the epididymis, which can cause infertility.
- Urethral Stricture: Narrowing of the urethra, leading to urinary problems.
Complications in Women
For women, untreated gonorrhea can lead to:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): A severe infection that can affect the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes, leading to infertility.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: This occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, posing serious health risks.
Complications in Both Genders
Both genders may face systemic infections if the bacteria spread through the bloodstream, leading to conditions like:
- Gonococcal Arthritis: Joint pain and inflammation can occur.
- Endocarditis: Infection of the heart lining can develop.
How to Diagnose Gonorrhea
If you suspect you have gonorrhea, it’s crucial to seek medical advice. Diagnosis typically involves:
- Urine Tests: A sample of urine can detect the presence of the bacteria.
- Swab Tests: A healthcare provider may take swabs from the affected areas, including the throat or cervix.
- Blood Tests: In certain cases, blood tests may be conducted to check for complications.
Importance of Regular Testing
Regular STI screenings are vital for sexually active individuals, especially if you have multiple partners. Early detection can help prevent complications and the spread of infection.
Treatment Options for Gonorrhea
If diagnosed with gonorrhea, effective treatment is available. Here’s what you need to know:
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are the primary treatment for gonorrhea. Healthcare providers typically prescribe a dual therapy, which includes:
- Ceftriaxone: An injection is commonly used to treat gonorrhea effectively.
- Azithromycin: An oral antibiotic that may be given in conjunction with ceftriaxone.
Importance of Completing Treatment
It’s crucial to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms disappear. Failure to do so can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Follow-Up Testing
After treatment, follow-up testing is essential to ensure the infection is cleared. This is especially important if symptoms persist or if you had sexual partners who may also need treatment.
Preventing Gonorrhea
Preventing gonorrhea is possible with the right strategies. Here are key preventive measures:
1. Practice Safe Sex
Using condoms or dental dams during sexual activity significantly reduces the risk of transmission. Make this a priority in your sexual encounters.
2. Get Regular STI Screenings
Routine screenings can help detect STIs before they cause complications. Regular check-ups are essential for sexually active individuals.
3. Limit Sexual Partners
Reducing the number of sexual partners decreases your risk of exposure to STIs, including gonorrhea.
4. Communicate with Partners
Open discussions about sexual health with your partners can promote safety and awareness. Ensure that both parties are informed about their STI status.
Conclusion: Stay Informed and Proactive
Recognizing gonorrhea symptoms early is vital for effective treatment and prevention of complications. Regular testing, safe sex practices, and open communication can significantly reduce the risk of gonorrhea and other STIs. If you experience any symptoms or have concerns about your sexual health, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Your health and well-being are worth the effort, so stay informed and proactive in your approach to sexual health.
REFERENCE : gacorx5000